LEARNING
ü Antimicrobial Agents
ü Antiseptic
ü Disinfectant
ü Germicide
ü Germistatic
ü Mechanism of action of anti-microbial agents
o Oxidation
o Halogenations
o Protein precipitation
What are Antimicrobial Agents?
· The chemical substances which can kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms are called Antimicrobial agents.
· Examples of Inorganic Antimicrobial agents most widely used are-
· Bleaching powder, Hydrogen peroxide, Potassium permanganate, Sodium hypochlorite, Iodine, Silver nitrate, Mercury, mercuric oxide, Sodium perborate.
Classification
Depending upon the activity of antimicrobial agents these may be classified as;
1. Antiseptics
· Any agent that either kill or inhibit the growth of microorganism (bacteria, fungi, virus, Protozoa) but these are only applied in the living tissue.
· Antiseptic agents oppose the sepsis, putrefaction or decay of the damaged or exposed tissue by inhibiting microbial multiplication and metabolic activities or by killing the pathogenic microorganism.
· This type of agents may be used in the form of mouth washes, soaps, deodorants, throat and nasal sprays and vaginal douches.
2. Disinfectants
· Any agent that either kill or inhibit the growth of microorganism (bacteria, fungi, virus, Protozoa) but these are only applied on inanimate objects(instruments, rooms, floor, rooms, equipment, Pond, river)
· They are non-selective and destroy non pathogens .also these are irritant and corrosive to the skin or tissue.
3. Germicide -(cide-Kill, latin caeder means to kill)
· These are the agents that kill the microorganism. The different terminology may be used for specific action of these agents.
· Bactericide-kill bacteria, fungicide-kill fungi, virucide – kill virus
4. Germistatic – (stat – standing till, Greek word stasis)
· These are the agents that do not kill microorganism but inhibit their growth.
· The term bacteistatic, fungistatic are used against the respective microorganism.
5. Sanitizers
· The antimicrobial agents which are used to maintain general public health standards.
· Characteristic of an Antimicrobial agents
o Should have antiseptic and germicidal activity.
o Should have faster onset of action.
o Should have better therapeutic index.
o Should not cause local cellular damage.
o Should not interfere with body defence mechanism.
o Should not show the systemic toxicity.
o Should have broad spectrum activity against bacteria, fungus, virus, and protozoa.
How the Inorganic antimicrobial agents are act?
Mechanism of action of Inorganic Antimicrobial agents
· Inorganic antimicrobial agents are shown their action any of the following three mechanism of action.
1. Oxidation
2. Halogenations
3. Protein precipitation
1. Oxidation
· Oxidative mechanism showing agents are generally non metals and certain types of anions.
· Example: hydrogen peroxide, metal peroxides, permanganates, halogens (chlorine, iodine) and certain oxo halogen anions.
· As the microbial proteins and enzymes are vital for the growth or survival of the microorganism.
· This types of agents are oxidised the reducing group (sulpha hydryl group-SH present in cysetein amino acid) of microbial proteins or enzymes, which leads to form a disulphide bridge in the protein and also changes it conformation (shape) and function.
· The overall changes of function of specific protein responsible for destruction of microorganism.

2. Halogenations Mechanism
· The compounds which liberate halogen (chlorine, iodine) or hypochlorite (OCl–) act by this mechanism.
· These types of compound doing halogenations of peptide linkage of specific protein or enzymes of microorganism.
· The substitution of halogen atom on peptide linkage of the protein, there is changed in H-bonding which is essential for protein structure and alteration of protein structure leads to dysfunction of specific protein enzyme function.

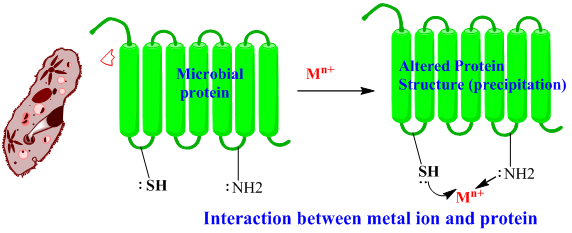
3. Protein Precipitation
· This type of mechanism of action is shown by the metallic ions having large charge/radius ratio or strong electrostatic fields.
· Example: metals of Groups IB, IIB (Cu, Ag, Zn, Al ions) and group IIIA metal ions.
· The microbial protein has different polar group such as -SH, -OH, -NH2, as these groups have lone pair of electron acts as ligand(electron donor) and metal ions act as Lewis acid(electron acceptor). The interaction between metal ions and such groups formed a chelate complex leads to protein precipitation and inactivation of vital protein causes the death of microorganism.
· Protein precipitation action is nonspecific so it acts on both host cell and microbes.

Hi…! Currently, I am working as an Professor at Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry(H.O.D),The Pharmaceutical College, Barpali, Odisha. I have more than 19 years of teaching & research experience in the field of Chemistry & Pharmaceutical sciences.
